



In the realm of modern engineering, the efficiency of cooling systems is critical for the optimal performance of machinery, particularly in automotive and industrial applications. According to a recent report by the International Thermal Management Society, efficient cooling solutions can enhance system performance by nearly 30%, which underscores the importance of effective thermal management. A pivotal component of these systems is the Motor Cooling Fan Blade, designed to circulate air and dissipate heat effectively.
Various types of Motor Cooling Fan Blades have emerged, each tailored to specific operational needs and environmental conditions. Research indicates that selecting the right fan blade type can significantly impact both energy consumption and overall system performance. For instance, advanced blade designs can improve airflow by up to 40%, leading to reduced energy usage and lower operational costs. As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability and efficiency, understanding the diverse range of Motor Cooling Fan Blade types becomes essential for engineers and operators aiming to optimize their cooling systems and improve their overall efficiency.
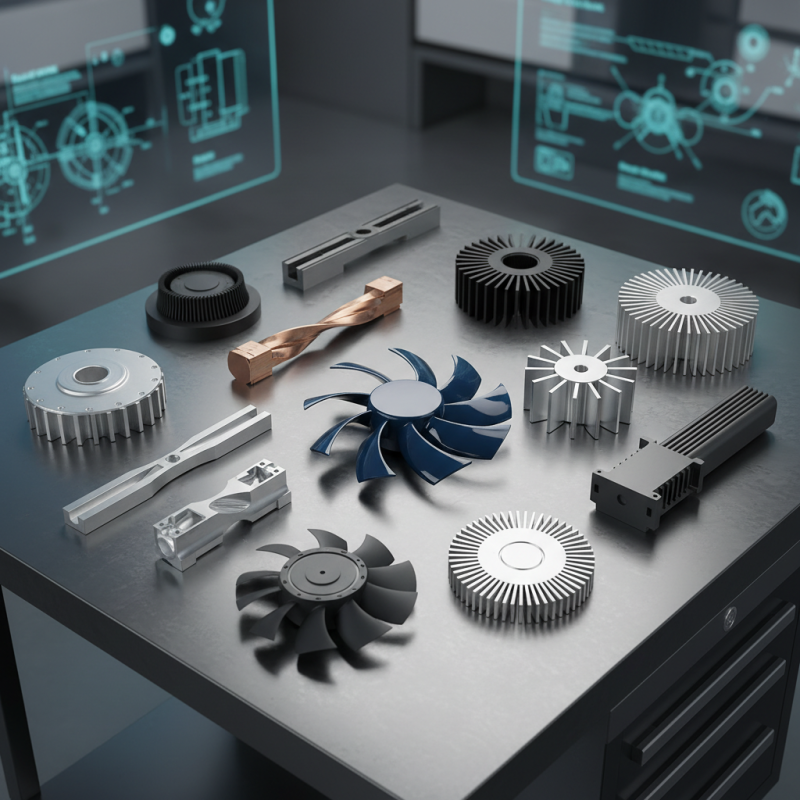
Motor cooling fan blades play a critical role in enhancing the efficiency of cooling systems across various applications, from automotive engines to industrial machinery. Effective blade design can significantly influence airflow dynamics and cooling performance. According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), optimizing the blade angle and profile can improve airflow by up to 25%, leading to decreased operational temperatures and increased longevity of machinery components.
Understanding the fundamentals of fan blade design involves evaluating factors such as blade shape, material, and size. For instance, research published in the Journal of Fluid Mechanics indicates that curved blades can create a more uniform airflow, reducing turbulence and increasing overall cooling efficiency. Furthermore, utilizing lightweight and durable materials, like reinforced composites, can improve thermal conductivity while minimizing the energy required to operate the fan. A study by the International Journal of Refrigeration highlights that advancements in blade design can lead to a reduction in energy consumption by 15%, essential for both economic savings and environmental sustainability in industrial settings.
When it comes to enhancing the efficiency of your cooling system, the type of fan blade you choose plays a significant role. Fan blades can be crafted from various materials, each offering unique advantages that can influence performance. For instance, plastic blades are popular for their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, making them a cost-effective option. In contrast, metal blades, often made of aluminum or steel, provide greater durability and strength, which can lead to improved airflow and cooling capabilities, especially in high-demand environments.
Tips: When selecting fan blades, consider the specific requirements of your cooling system. For instance, if weight is a crucial factor, look for blades made from high-performance plastics. On the other hand, if you prioritize longevity and robustness, investing in metal blades might be the better choice.
Beyond material, the design of the fan blades is equally crucial. Blades with a greater pitch can move more air, making them suitable for systems that require high airflow rates. However, designs with a lower pitch often operate more quietly and may be more efficient at lower speeds. Understanding the application and environment of your cooling system will help you select the optimal fan blade type to improve overall efficiency.
Tips: Always consider environmental factors such as temperature extremes and exposure to moisture when choosing materials. This foresight will help ensure the longevity and effectiveness of your fan blades, further enhancing your cooling system's performance.
Dynamic blade shapes in motor cooling fans play a crucial role in enhancing airflow while minimizing noise levels. Recent studies indicate that fan blade design can influence airflow efficiency by up to 30%. This improvement is particularly significant in applications where managing heat is critical, such as in automotive and industrial machinery. Innovative designs, including curved and angled blade shapes, are engineered to optimize the airflow patterns. By aligning the blades strategically, manufacturers can achieve better air velocity and pressure distribution, which aids in cooling performance without amplifying sound.
Moreover, noise reduction has become a pivotal focus in fan design. According to the International Society of Automation, excessive noise levels can hinder environmental comfort and workplace productivity. Advanced blade geometries and materials have led to reductions in operational noise by 20% or more through the minimization of turbulence and drag. Enhanced airflow dynamics not only improve cooling efficiency but also contribute to a quieter operational environment. Such advancements highlight the significance of thoughtful engineering in fan design, addressing both performance and noise concerns, which is essential for modern applications.
When it comes to motor cooling fan blades, one of the pivotal considerations is the angle of the blades, which can significantly impact the efficiency of the cooling system. Fixed blade angles offer simplicity and reliability. They are designed to provide consistent airflow and cooling performance across a range of operational conditions. However, the downside is that they lack adaptability; fixed angles may not optimize airflow in varying environmental conditions, potentially leading to either excessive energy use or insufficient cooling.
On the other hand, adjustable blade angles present a more dynamic solution. These fans can adapt to changing conditions, allowing for optimal airflow and cooling efficiency depending on the temperature and load requirements. By altering the blade angles, adjustable fans can reduce energy consumption when high airflow isn’t necessary and increase cooling power during peak operational periods. This versatility can result in better overall performance and lower operational costs. The performance comparison between fixed and adjustable blade angles indicates that while fixed blades serve well in consistent environments, adjustable blades provide more efficient cooling in fluctuating circumstances, making them a compelling choice for modern cooling systems.
| Blade Type | Blade Angle Type | Cooling Efficiency (%) | Noise Level (dB) | Material |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | Fixed | 85 | 30 | Plastic |
| Type B | Adjustable | 90 | 28 | Aluminum |
| Type C | Fixed | 78 | 34 | Composite |
| Type D | Adjustable | 92 | 26 | Steel |
| Type E | Fixed | 80 | 32 | Plastic |
| Type F | Adjustable | 88 | 29 | Aluminum |
| Type G | Fixed | 75 | 36 | Composite |
| Type H | Adjustable | 91 | 27 | Steel |
| Type I | Fixed | 82 | 31 | Plastic |
| Type J | Adjustable | 94 | 25 | Aluminum |
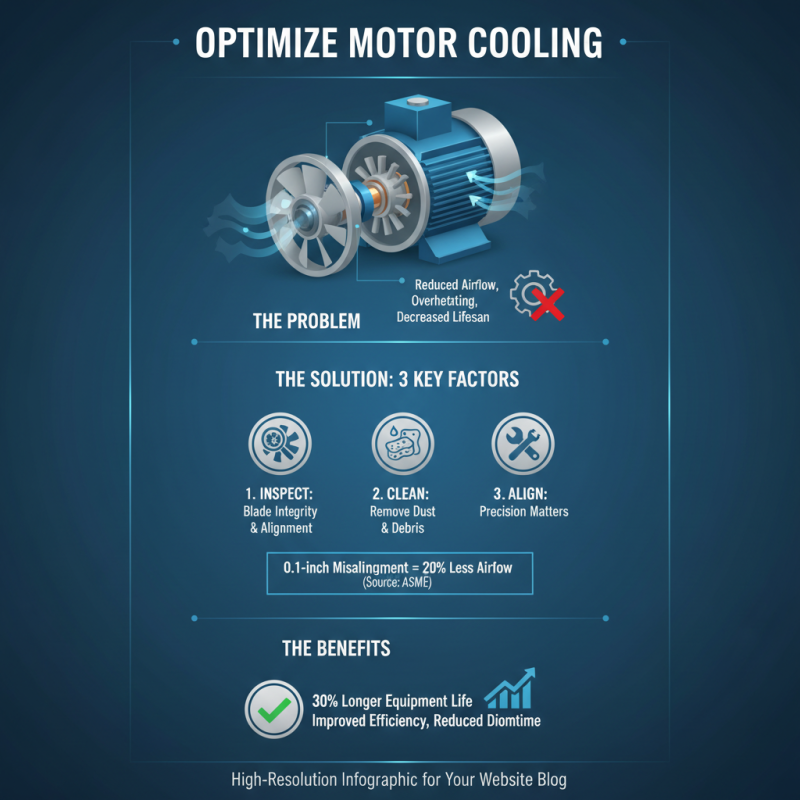
Maintaining the functionality of cooling fan blades is essential for optimizing the efficiency of motor cooling systems. Proper maintenance can lead to significant improvements in system performance, with studies indicating that a well-maintained cooling system can enhance equipment longevity by as much as 30%. Regular inspections focused on blade integrity, cleanliness, and alignment are key factors in ensuring operational efficiency. For instance, a report from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) suggests that a mere 0.1-inch misalignment can lead to a 20% reduction in airflow, impacting cooling effectiveness considerably.
In addition to alignment, the cleanliness of cooling fan blades plays a crucial role in their functionality. Dust and debris accumulation can restrict airflow, leading to overheating and increased energy consumption. A maintenance routine that involves cleaning the blades at regular intervals can yield a notable decrease in energy usage, as detailed in a study by the Energy Efficiency Partnership. They found that systems with cleaned fan blades operated 15% more efficiently compared to those with accumulated grime. Implementing these maintenance practices not only saves energy but also reduces maintenance costs in the long run, ultimately contributing to a more efficient cooling system.