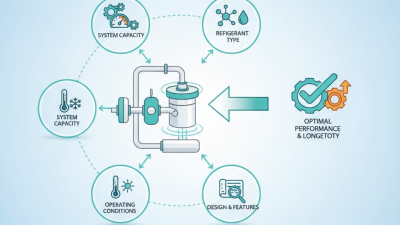




Capillary copper is a remarkable material used in various applications. Its unique properties make it highly effective in transferring heat and fluids. Many industries rely on capillary copper for enhanced performance and efficiency.
This material is often used in cooling systems, electronic devices, and medical equipment. The ability of capillary copper to conduct heat faster than other materials is invaluable. Engineers appreciate its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion.
Yet, challenges persist in its application. Manufacturing processes can be complex, and costs may be higher compared to alternatives. Some users report difficulties in integrating capillary copper into existing systems. Despite these concerns, the benefits often outweigh the drawbacks.
Capillary copper is known for its versatility in various applications. One significant area is in electronics. The unique properties of capillary copper make it ideal for heat transfer. It efficiently absorbs and dissipates heat. This helps to enhance the performance and longevity of devices. In smartphones, for example, capillary copper is used to manage heat more effectively.
Another important application is in plumbing systems. Capillary copper’s excellent corrosion resistance ensures durability and reliability. This makes it suitable for hot and cold water pipes. It can also be used in heating systems. However, not all installers understand the nuances of working with capillary copper. Missteps can lead to leaks or inefficient systems.
In the medical field, it has significant potential. Capillary copper is utilized in some medical devices and tools. These devices need precision and reliability. Yet, challenges remain in ensuring consistency in manufacturing. Fluctuations in quality can affect performance and safety. Despite these hurdles, the advantages of capillary copper continue to drive its innovation and application in various sectors.
| Application | Description | Benefits | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Exchangers | Devices that transfer heat between two or more fluids. | High thermal conductivity, compact design. | HVAC systems, automotive radiators. |
| Capillary Tubes | Small-diameter tubes used in refrigeration systems. | Improved flow control, cost-efficient. | Refrigerators, air conditioners. |
| Welding Rods | Filler material for joining copper and copper alloys. | Strong joints, excellent corrosion resistance. | Electrical connections, plumbing. |
| Jewelry Making | Using capillary copper to create intricate designs. | Malleable, easy to shape and solder. | Fashion accessories, custom pieces. |
| Electronics | Wiring and printed circuit board applications. | Excellent conductivity, durable. | Smartphones, computers, home appliances. |
Capillary copper has gained attention across various industries for its unique properties. Its ability to conduct heat efficiently makes it ideal for applications in electronics and automotive sectors. The fine capillaries allow for efficient fluid movement, crucial in cooling systems. This enhances performance and safety in engines and machinery.
In the medical field, capillary copper is valuable for its antimicrobial properties. It helps reduce infection rates in hospitals. The durability of copper supports its use in equipment that can withstand rigorous cleaning. However, the high cost of production can limit its widespread application.
Tips: Always consider the application environment. Capillary copper may not perform well in highly corrosive settings. Regular maintenance is needed to ensure longevity. Additionally, assess the heat transfer requirements before selecting your materials. Balancing cost and performance is essential.
Capillary copper has unique applications in electrical engineering. This material is known for its excellent conductivity. Engineers often use it to create fine wires in compact circuits. Capillary copper excels in spaces where traditional wires cannot fit. Its ability to withstand heat is another advantage. High temperatures do not compromise its conductivity.
In electronics, capillary copper is used in connectors and coils. These components benefit from the material's lightweight nature. This makes devices more portable. However, working with capillary copper can be challenging. It requires precise handling due to its thin gauge. Sometimes, the flexibility may lead to unintended bending. Designers must constantly assess compatibility with other materials.
Another common application is in sensors. Capillary copper allows for quick responses in temperature and pressure sensing. This responsiveness enhances device reliability. There is still room for improvement in durability, as capillary structures can be fragile. Moreover, the cost of processing capillary copper might outweigh its benefits in some projects. So, weighing the pros and cons is essential for engineers.
This chart illustrates the various applications of capillary copper in electrical engineering. The data represents the percentage usage of capillary copper across different applications, highlighting its significance in electrical connectors and wiring.
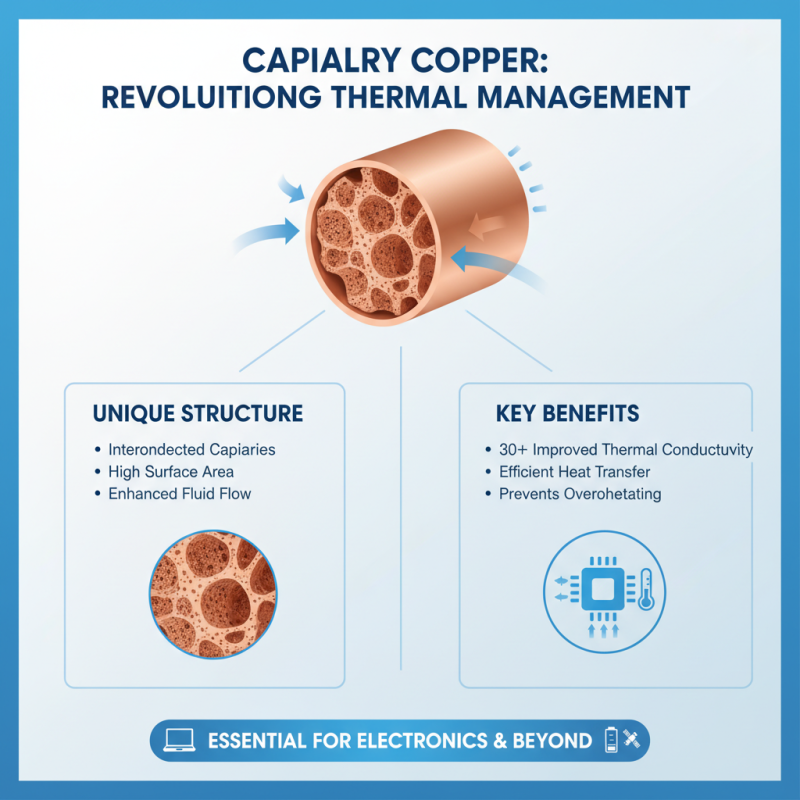
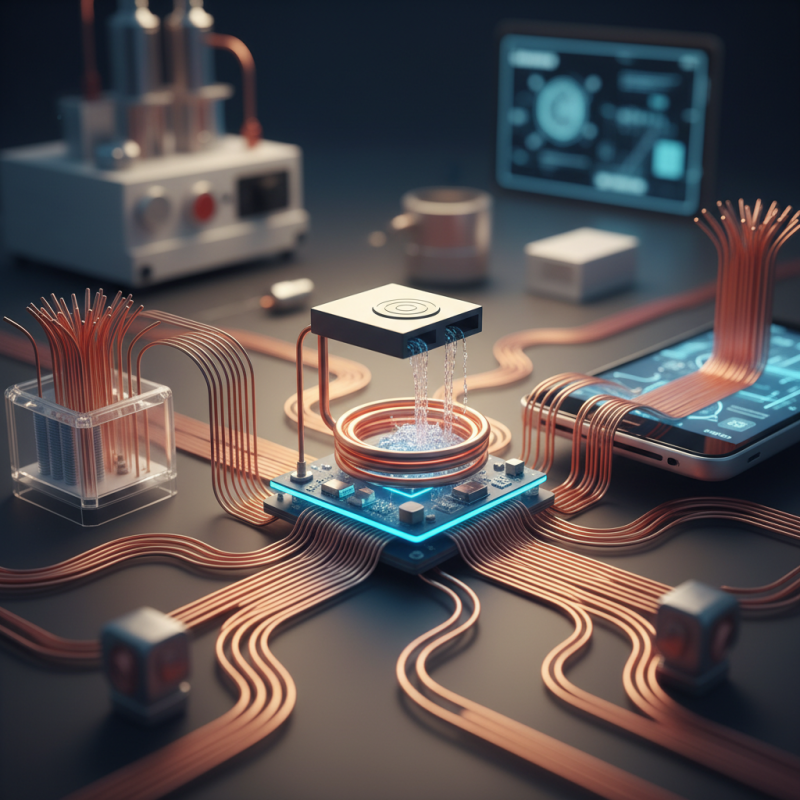
Capillary copper plays a crucial role in thermal management. Its unique structure allows efficient heat transfer, essential for various applications. According to recent industry reports, capillary copper can improve thermal conductivity by over 30% compared to traditional materials. This benefit is vital in electronics, where overheating can lead to failure.
Efficient thermal management is critical in high-performance devices. The use of capillary copper enhances the reliability of components, like CPUs and GPUs. However, manufacturing processes often face challenges. Achieving uniform capillary structures is demanding. According to the International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, inconsistencies can reduce effectiveness by up to 15%.
Innovative designs using capillary copper offer promising solutions. They can be integrated into cooling systems, especially in renewable energy technologies. Yet, some implementations still face hurdles. Material fatigue, often overlooked, can impact long-term performance. Continuous research and development are necessary to maximize the benefits of capillary copper.
The field of capillary copper technology is witnessing rapid advancements. New methods are enhancing the thermal conductivity and flexibility of capillary systems. Engineers are experimenting with new manufacturing techniques that promise improved efficiency. These innovations aim to revolutionize applications in electronics and renewable energy.
Miniaturization is a key trend. Smaller components are becoming more prevalent in technology. This pushes the boundaries of traditional capillary copper applications. With precise engineering, these systems can fit into tighter spaces. However, the challenge remains in ensuring reliability and performance under varied conditions.
The future may also hold smart materials integrated with capillary copper. Imagine systems that can self-regulate temperature. Such advancements could lead to significant energy savings. Yet, this ambition raises questions about durability and cost. Refining these technologies is essential for practical applications. Balancing innovation with sustainability remains a critical challenge in this evolving landscape.